[Modern Java In Action] 13. 디폴트메서드
in Programming on Java
이 장에서는 Default Method가 무엇인지, 어떻게 활용하는지 알아본다.
13.1 변화하는 API
나는 자바 라이브러리 개발자로, 예전에 인터페이스 API v1 를 포함한 라이브러리를 배포했다. 그런데 추가할 메서드가 생겨서 인터페이스 API v2 라이브러리를 배포했다. 내 라이브러리를 사용하던 유저들은 괜찮을까..??

예전의 자바라면…? 내 인터페이스를 사용하던 사람들의 표정이 좋지않다.☹️
내가 v2에 추가한 메서드를 사용하지 않는 사용자들도, 반드시 이 메서드를 구현하도록 클래스를 고쳐야지만 에러가 안난다. 업데이트와 함께 에러가 발생하고 쓰지도 않을 기능때문에 코드를 고치게된 사람들의 불만이 폭주한다.
자바8에서는…? 이런 사용자들의 불편을 막기 위해 defalt method가 나왔다. 내가 v2에 메서드를 추가할때 default method로 구현하면 사용자들은 디폴트 메서드의 구현을 자동으로 상속받게되어 굳이 구현을 하지 않아도 된다. 😊
1) Default Method
<API v1>
개발자는 Resizable 라는 인터페이스를 만들었다.
public interface Resizable extends Drawable{
int getWidth();
int getHeight();
void setWidth(int width);
void setHeight(int height);
void setAbsoluteSize(int width, int height);
}
사용자는 이걸 활용한 Ellipse 라는 클래스를 만들었다.
public class Ellipse implements Resizable {
...
}
<API v2>
개발자는 v2로 버전업을 하면서 setRelativeSize 라는 메서드를 추가함
public interface Resizable {
int getWidth();
int getHeight();
void setWidth(int width);
void setHeight(int height);
void setAbsoluteSize(int width, int height);
void setRelativeSize(int wFactor, int hFactor); // v2 에서 추가
}
→ 이러면 v1을 구현해 Ellipse 를 생성했던 사용자는 에러를 겪게된다.
default void setRelativeSize(int wFactor, int hFactor){
setAbsoluteSize(getWidth() / wFactor, getHeight() / hFactor);
}
→ 하지만, 위와 같이 ‘구현’을 가지는 default 메서드로 선언해주면 에러를 겪지않는다.
이렇게 디폴트 메서드를 이용하면 라이브러리를 바꿔도 호환성을 유지할수있다.
3) 정적메서드 구현
디폴트메서드랑 별개로, 자바8에서는 인터페이스에 직접 정적메서드 선언할수있게 해줬다. 따라서 유틸리티클래스 없이 직접 인터페이스내부에 정적메서드 구현해서 사용해도됨!
static setRelativeSize(int wFactor, int hFactor){
setAbsoluteSize(getWidth() / wFactor, getHeight() / hFactor);
}
13.3 디폴트 메서드 활용패턴
또 다른 활용패턴도 있다
1) 선택형 메서드
인터페이스 내에 사용자들이 잘 사용하지 않는 메서드가 있을 수 있다. 사용자 입장에서는 쓰지도 않을걸 구현하니 짜증이난다. 이때 또 default method를 사용해 기본구현을 제공하여 사용자가 빈구현을 만들지 않게 배려해주자.
interface Iterator<T> {
boolean hasNext();
T next();
// 사람들이 잘 안쓰는 remove는 default method로 기본구현을 제공해주자
default void remove() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
}
2) 동작 다중 상속
default method를 이요하면 기존에는 불가능했던 동작 다중상속 기능도 구현 가능!
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E> // 상속 (1개만가능)
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, Serializable { // 구현 (여러개가능)
}
여러 인터페이스의 동작를 상속받을수 있게 되는 셈.
→ 각각 모듈이 최소한의 인터페이스를 유지한다면 우리코드에서 쉽게 재사용/조합이 가능하다
13.4 해석 규칙
근데 이렇게 동작의 다중상속이 가능하면, 여러 인터페이스에서 같은 시그니처를 가지는 디폴트메서드를 동시에 상속받는 상황에서는 어떻게될까? 아래 3가치 규칙대로 순위가 결정된다.
- 클래스가 항상 이긴다. 클래스/슈퍼클래스에서 정의한 메서드가 디폴트메서드보다 우선권을가진다
- 1번 외 상황에서는 서브인터페이스가 이긴다. (B가 A를 상속받는다면 B가 이김)
- 여전히 우선순위가 모호하다면 상속받는 클래스가 명시적으로 디폴트메서드를 오버라이드하고 호출해야함
이제 예제로 이해해보자
1) 디폴트메서드를 제공하는 서브인터페이스가 이긴다
public interface A {
default void hello() {
System.out.println("Hello from A");
}
}
public interface B extends A {
default void hello() {
System.out.println("Hello from B");
}
}
그림으로 보면 이런상황이다
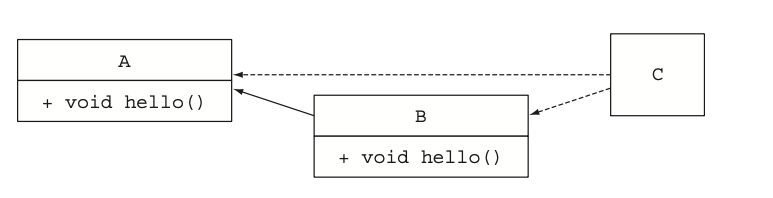
2번규칙(디폴트메서드를 제공하는 서브인터페이스가 이긴다)에 의해 A를 상속받는 서브인터페이스B가 이겨서, Hello from B 가 출력된다.
그런데 조금 더 복잡해진다면?
public interface A {
default void hello() {
System.out.println("Hello from A");
}
}
public interface B extends A {
default void hello() {
System.out.println("Hello from B");
}
}
public class D implements A{ }
public class C extends D implements B, A {
public static void main(String... args) {
new C().hello();
}
}
그림으로보면 이렇다
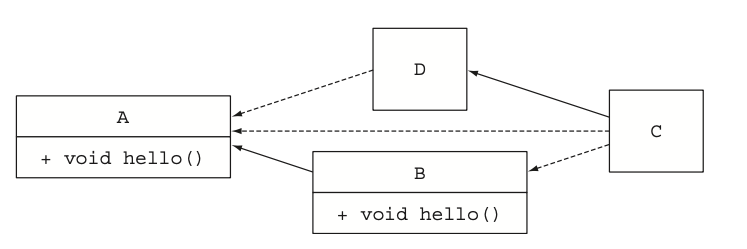
1번 규칙에 의해 D가 이길줄알았는데 D를 보면 hello 오버라이드하지않고 구현만한상황. → A의 디폴트메서드 구현을 상속받음.
A의 default method VS 서브인터페이스 B의 default method 싸움이되면서 B가 이겨서 Hello from B 가 출력됨
2) 클래스가 이긴다
public class D implements A{
void hello(){
System.out.println("Hello from D");
}
}
이런식으로 D가 A의 메서드를 오버라이드한 상황이면?
규칙1(클래스가 이김)에의해 슈퍼클래스 D 의 hello method VS B의 default method 싸움이 되면서 D가 이겨서 Hello From D 가 출력됨.
3) 충돌과 명시적해결
public interface A {
default void hello() {
System.out.println("Hello from A");
}
}
public interface B {
default void hello() {
System.out.println("Hello from B");
}
}
public class C implements B, A { }
이런상황이 되면 자바 컴파일러가 어떤 메서드를 호출할지 모호하기때문에 에러가나옴
Error: class C inherits unrelated defaults for hello() from types B and A.
해결하려면 아래와 같이 X.super.m(...) 형태로 어떤 인터페이스를 호출할지 명시해줘야한다
public class C implements B, A {
void hello(){
B.super.hello();
}
}
4) 거의 비슷한 시그니쳐
public interface A{
default Number getNumber(){
return 10;
}
}
public interface B{
default Integer getNumber(){
return 42;
}
}
public class C implements B, A {
public static void main(String... args) {
System.out.println(new C().getNumber());
}
}
이런상황엔 어떨까? (시그니쳐가 Number / Integer 로 다르긴함..)
→ C는 A/B를 구분하지 못하고 컴파일 에러가난다
5) 다이아몬드문제
public interface A{
default void hello(){
System.out.println("Hello from A");
}
}
public interface B extends A { }
public interface C extends A { }
public class D implements B, C {
public static void main(String... args) {
new D().hello();
}
}

이런 다이아몬드에서는 어떨까?
→ A만 default method가 존재… 고민할것도 없이 Hello from A 출력
만약 B에도 같은 시그니처의 default method가 있다면?
→ B가 이김 (규칙2. 서브인터페이스가이김)
B,C 모두 같은시그니처 default method가 있다면?
→ D가 명시적호출해줘야됨. (규칙3)
