Onboard Observation Task Planning for an Autonomous Earth Observation Satellite Using Long Short-Term Memory
in Data Science on Paper
Onboard Observation Task Planning for an Autonomous Earth Observation Satellite Using Long Short-Term Memory
LSTM을 이용한 지구관측위성의 Onboard Observation Task planning.
Authors
SHUANG PENG, HAO CHEN, CHUN DU, JUN LI, AND NING JING College of Electronic Science, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha, 410073 , China Corresponding author: Hao Chen (e-mail: hchen@nudt.edu.cn).
중국국방기술대학에서 낸 논문이다.
Abstract
Onboard observation task planning plays an essential role in satellite autonomy, which has attracted considerable attention from researchers in recent years. Most of the existing studies solve the satellite onboard observation task planning problem (SOOTP) by searching algorithms. However, the limited computing resources and the changes of onboard condition present a new challenge for these methods. In this paper, we develop a sequential decision-making model and propose a deep learning based planning method to solve the SOOTP. Instead of generating a short-term or long-term plan in advance, the sequential decision-making model enables the satellite to decide the observation task to execute in real-time. In the deep learning based planning method, a long short-term memory based encoding network is designed to extract the features and a classification network is used to make such a decision. In the experiment, we compared our method with the gated recurrent unit network and other three searching algorithms based on five scenarios. The experimental results show that our method can solve problems with 90.3%−93.7% accuracy, 2.19%− 3.95% profit gap, and 0.004s − 0.006s response time per task, which confirms its feasibility.
(1) Satellite onboard observation task planning problem (SOOTP*) 해결을 위한 순차적 의사 결정 모델을 구축하고 딥러닝 기반의 planning 기법을 제안
(2) 미리 단기/장기 plan을 세우는 것이 아닌, 순차적 결정을 통해 실시간으로 위성이 observation task를 수행할지 말지에 대한 결정을 가능케 함
(3) Task 실행 여부 분류에 필요한 특징 추출을 위해 LSTM 기반의 encoder를 구축
(4) 다섯 가지 시나리오를 토대로 본 논문에서 제시한 모델의 성능과 GRU 및 세 가지 탐색 알고리즘의 성능을 비교한 결과, 본 논문에서 제시한 모델이 다수의 시나리오에서 GRU와 동등하거나 우월한 성능을 보임.
Keyword
satellite autonomy, onboard observation task planning, sequential decision-making, deep learning, long short-term memory
Introduction
적은 ground control에서 점점 더 증가하는 갯수의 satellites들을 관리하다보니, satellite와 ground control간에 communication시 bottleneck이 존재함. 이를 해결하기 위해 onboard ask planning이 필요.
SOOTP는 satellite autonomy에서 매우 필수적인 역할. 대부분의 연구자들은 SOOTP를 최적화 문제로 판단하고 searching algorithm으로 문제를 풀었음. 이때 접근방법에 따라 아래와 같아 2가지 카테고리로 나뉨.
(1) batch-based planning approach
batch process로 스케쥴이 구성됨. onboard planner는 observation task를 비교적 long term 으로 구성함. (one to several days)
조건(환경)이 바뀌면 새로운 plan을 다시 개발해야됨. 제한된 리소스안에서 계산해야하기때문에 매우 computational intensive process (계산집약적프로세스)라서 새로운 plan을 짜는데 time delay가 생길수밖에 없음.
(2) rolling/continuous planning approach.
변화가 일어났을때 동적으로 plan을 수정할 수 있음. long-term planning horizon을 multiple overlapping short-term planning horizon으로 쪼갬. 이 short-term planning horizon에 기반하여, planner는 일관성을 유지하면서 satellite의 상태(energy level, data level 등..)에따라 새로운 계획을 세움.
참고하면 좋은 문헌)
Using iterative repair to improve the responsiveness of planning and scheduling,” in International Conference on Artificial Intelligence Planning Systems
CASPER에 사용된 지속적인 수정, 업데이트가 되는 plan을 support하는 rule-based iterative repair algorithm
대부분의 연구를 보면 좋은 repair stategy를 찾아야 동적으로 plan을 잘 수정해서 좋은 퀄리티의 solution을 얻을 수 있음. rolling/cobtinuous planning approach도 즉시 계획을 세울수있는 능력이 필요함.
만약 onboard-planner가 실시간으로 task를 결정해서 실행할수있다면 AEOS는 매우 발전할것임. RNN은 sequence data를 다루는데 매우 파워플한 딥러닝 모델이므로 이것이 위성의 raw sequence data(Observation task data)를 분류하는데 큰 도움을 줄수있을것. 여태까지는 SOOTP에 그런 알고리즘이 적용된적이 없음.
이 논문에서는 SOOTP를 sequential decision-making problem으로 가정하고 이것을 planning algorithm에 기반한 deep learning으로 문제를 해결할것임.
main contribution
(1) develop a sequential decision-making model for the SOOTP.
(2) design a LSTM based encoding network, and classification network to decide wheter a task shold the executed.
Satellite onboard observation task planning problem

(1) observation task : collect images
(2) transmission task : download the stored images
Energy는 observation task, transmission task가 일어날때 소모됨.
Memory는 observation task때 할당되고 transmission task가 일어날때 해제됨.
ground station은 여러 satellites들로부터 이미지를 받을수 있으므로, data collision을 막기 위해 각 satellite의 transmission task가 ground control center에 의해 미리 할당되어야함.
사용되는 이미지가 매우 커서 onboard observation task는 매우 엄격해야하고 효율적인 decision making이 필요함.
Sequential decision-making model
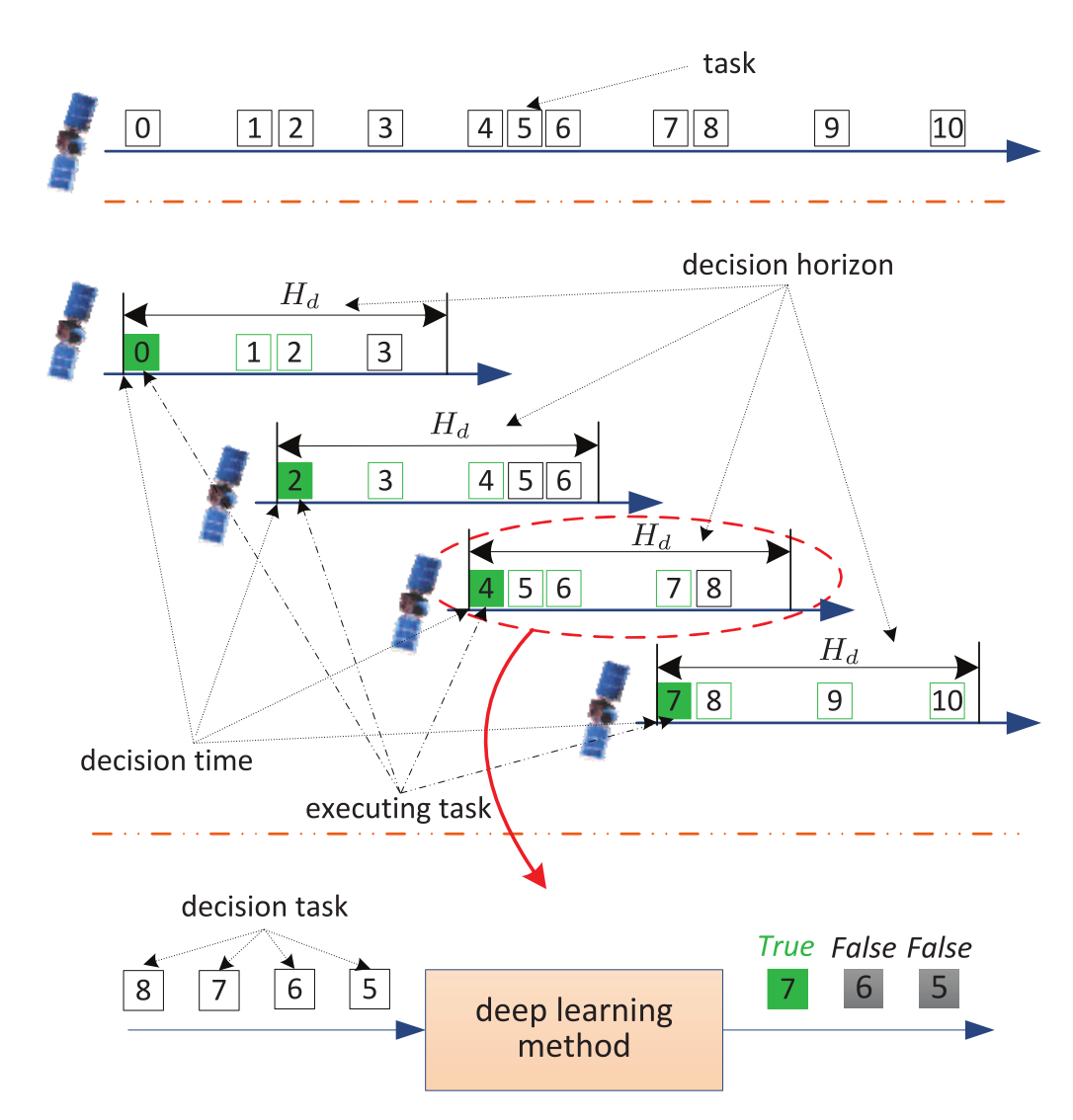
새 observation task나 기대치못한 energy, memory문제, 구름존재 등의 환경변화에 빠르게 대처하려면 sequential decision-making model을 만들어야함.
현재 task의 시작 시점에 dicision horizon 내의 best observation task를 찾고, 그 task가 다음 decision time에 수행되는 구조. planner는 decision result가 True가 될때까지 decision horizon에서 observation task를 하나씩 판단해나가는데, 이때 결정된 observation task의 start time이 다음 new decision horizon의 start time이 되는것이다.
이때 task들은 decision task에서 결정된다. decision horizon 내에 결정된 task가 없다면 다음 decision time으로 넘어간다.
예) 그림에서 task 4가 결정되어 executing되는 순간, task 5,6,7,8이 decision task안에서 deep learning model에 의해 판단당하게된다. task 7이 True로 판명되는 순간, task 7은 다음 실행 task가 되고 task 7의 start time에 새로운 decision time이 시작된다.
Deep learning based planning method

LSTM이 sequence data를 학습하는데 매우 뛰어난 모델이므로 LSTM에 기반한 deep learning model을 우리의 문제에 적용해보도록 한다.
encoding network + classification network
Encoding Network
look-ahead horizon 안의 decision task의 subsequent task를 2개의 LSTM을 통해 fixed length vector representation 으로 encoding한다.
encoding network는 한마디로 look-ahead horizon의 feature extractor이다. look-ahead horizon 안의 decision task를 발라내기 위해 L-LSTM(Local LSTM). G-LSTM(Global LSTM)을 사용한다.
L-LSTM은 deicision task와 confilct가 있는 task를 읽는다.(conflicting task) planner가 decision task와 다른 observation task간의 degree of conflict를 판단할 수 있도록한다. G-LSTM은 look-ahead horizon의 rest of tasks를 읽는다. (non-conflicting task) planner가 short-sighted decision을 내리는것을 막는다.
GL-LSTM에서 conlfict task는 먼저 제거되고, rest of the task는 conflicting task(L-LSTM)와 non-conflicting task(G-LSTM),이렇게 2개 part로 나뉜다. 또한 이는 Energy, Memory, Setting time 제약조건을 따른다.
실험에 따르면 이 GL-LSTM은 그냥 LSTM보다 feature를 잘 뽑아내는것으로 나타났다.
우리의 목적은 total profit을 maximize하는것이므로 PTGS(Profit-based Task Greedy Sampling) strategy를 샘플링할때 사용하였다.
Classification Network
structed representation에 기반하여 예측하고 가능성을 제공한다.
분류를하기위해 L-LSTM과 G-LSTM의 마지막 hidden state가 input으로 사용된다.
classification network는 single-layer linear neural network다. GL-LSTM으로부터 얻어진 representation을 기반으로 label을 붙인다. 학습을 위해 cross entropy 를 loss function으로 사용하였고 p(y,X)는 샘플X의 gold one-hot distribution으로 activation function인 softmax함수에 의해 결정된다.
Conclusion
이 논문은 autonomous earth observation satellite의 onboard observation task planning problem에 대한 연구이다.
우리는 sequential decision making model과 실시간 deep learning기반 planning method를 개발하였다.
미래의 우리 연구는 reinforcement learning method를 SOOTP에 적용해보는것이다. 매우 거대한 데이터를 학습시켜야하는데 거대한 데이터를 얻기힘든데, 강화학습을 사용하면 이 문제를 해결할수있다.
